Many people have had lower back discomfort. The low back problems can prove extremely painful and, in extreme instances, can affect the quality of life.
What causes it? Which category of people is most likely to suffer from back pain? Doctor. Joshua Li, an associate professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Virginia, spine surgeon, and who has an advanced doctorate degree in research on bone minerals provided a thorough explanation and presented the methods of treatment for lower back discomfort.
The anatomy of the Spine
To fully understand lower back discomfort, one must first know what is the structure of the spine and the tissue that is associated with it. The spine is composed of four components that include vertebrae, intervertebral discs muscles, nerves, and muscles.
The spine is further divided into four parts including cervical, thoracic sacral, and lumbar. The vertebrae comprise seven within the cervical spine as well as a curvature that is convex towards in front. there are 12 vertebrae within the thoracic spine while the curvature runs concave toward back of body. There are 5 vertebrae inside the lumbar spine which curvature convex towards forward of your body. The curvature created by the aligning with the spine is vital. An excessively outward or inward arch could cause difficulty standing up and poor posture.
The intervertebral discs sit within the bodies of vertebrae. They are circular and flat in their structure. Each disc is between one and three millimeters in thickness. The intervertebral disc is composed from two parts comprising the jelly-like nucleus pulposus, and the outer elastic annulus fibrous. The purpose of intervertebral discs are to cushion the shocks that are generated by movement.
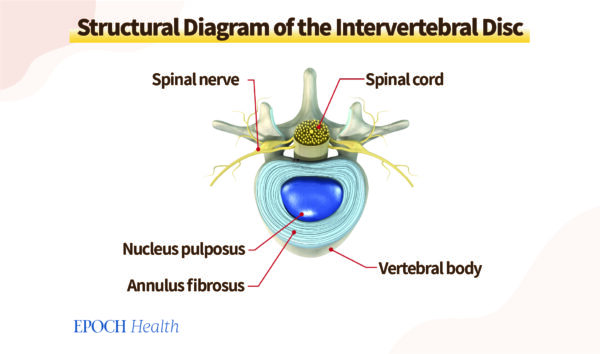 Intervertebral discs are able to help cushion the impact of the movement. (The Epoch Times)
Intervertebral discs are able to help cushion the impact of the movement. (The Epoch Times)The vertebral bodies join in order to create a channel that carries the spinal cord located at the rear. This safeguards the spinal cord. Each vertebra is connected the vertebral arch. the arrangement of arches form the intervertebralforamen from where spinal nerves expand, controlling motor and sensory information within the extremities.
The spine is covered by muscles. Strong muscles alleviate pressure from the vertebrae, as well as provide support to the spine to ensure that it remains in the right posture.
Issues with any of the vertebrae intervertebral discs or nerves and muscles could result in lower back discomfort.
What Group of People Is Prone to Back Pain in the Lower Back?
There are three categories of people who are especially vulnerable to lower back pain.
1. People whose work involves carrying
Construction workers and delivery workers frequently have to carry massive loads over and over again.
2. The job of a driver.
Truck drivers’ spines as well as taxi drivers are frequently subject to vertical vibrations and the stress can be concentrated around the discs of intervertebral which could cause deformation of the intervertebral discs.
3. Office worker
They are prone to bad posture, and they are often sedentary and this causes over-loading on the lower lumbar spine as well as the progressive flattening of intervertebral discs. This causes lower back discomfort.
4 Lower Back Pain Causes
1. Acute lumbar spinal injury
This is especially prevalent for young people since they tend to be more engaged in intense sports like badminton, volleyball and so on.
The back muscles of people are often stretched and twist during vigorous exercises, which can lead to muscle strain that is acute as well as damage to muscle fibers, microvascular rupture, and various issues that can cause muscle spasms.
2. Herniation of the disc
The outer annulus fibrous of the disc intervertebral looses its elasticity and strength, inside nucleus pulposus can be able to break through the annulus fibrousus and protrude. This causes the herniation of the intervertebral disc.
The structure of the whole intervertebral disc is akin to an everyday snack–a jelly donut. The nucleus pulposus looks like jelly and the annulus fibrosus is similar to the donut. an injured disc is similar to jelly that is squeezed out of the donut.
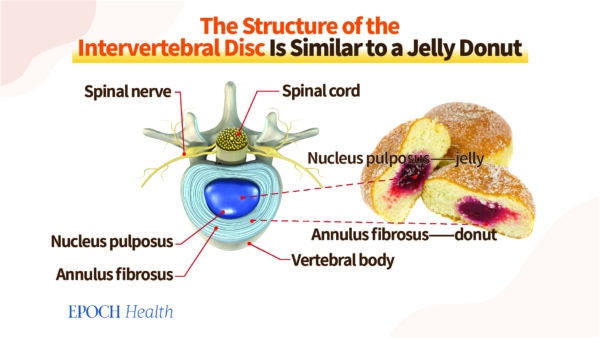
 Herniated disk is similar to jelly that is squeezed out of donuts. (The Epoch Times)
Herniated disk is similar to jelly that is squeezed out of donuts. (The Epoch Times)As the nucleus of the pulposus ruptures the intervertebral disk becomes less supple which means it loses cushioning capability. vertebrae are more likely be in collision when performing activities, causing lower back discomfort.
A protruding nucleus pulposus could cause lower back pain when it presses on the sciatic nerve. For instance, sciatica refers to numbness and discomfort within the lower back and lower limbs, caused due to a disc herniation that compresses the sciatic nerve and may cause weakness of the muscles.
A herniated disc could also cause inflammation.
The intervertebral discs are devoid of blood supply, and the immune system is unable to detect the nucleus pulposus. Therefore, it will recognize the protruding nucleus pulposus as a foreign tissue and will send antibodies to fight the disc in the intervertebral space which causes inflammation. The inflammation that causes irritation to nerves may also trigger discomfort.
Surprisingly enough, herniated discs tend to be more prevalent among younger people!
The primary reason is that young people tend to be more likely to lift heavier objects, which means they are more likely to suffer injuries. Another reason is that the nucleus pulposus in younger people has a an abundance of fluidity and water which means it is most likely to extend. the nucleus pulposus in the older people has a lower water content and is comparatively solidified, which means the likelihood of protrusion is lower.
3. Spinal Stenosis
If discs in the intervertebral space do not have enough strength to support its stability spine due to degeneration the surrounding tissues expand to shield nerves.
The expansion of ligaments and facet joints surrounding the spine could lead to closing of the spinal canal, which will further compress the nerves.
People who are older tend to be affected by spinal stenosis. A frequent sign is “intermittent claudication”–the patient’s legs as well as their lower back are prone to pain after walking a short distance, and they need to lie down and rest for a time to ease the pain before they can continue to walk.
Another sign that you have spinal stenosis is having trouble standing straight. The size of spinal canal decreases when one stands up straight. Thus, people with spinal stenosis tend to lean forward as it increases the volume of spinal canal and decrease nerve compression as well as lessen the pain. This is the reason that older people frequently hunch over and use crutches.
4. Compression fracture
The condition is serious and requires special attention. problem which requires specific attention.
Compression fractures are common among those who are elderly, particularly postmenopausal women. The majority of this group suffers from osteoporosis and their bones are quite fragile. When lifting heavy objects or falling over when leaning forward could result in fractures on the front vertebrae.
In the image of X-rays below, it is evident how the frontal length of the first vertebra shorter, while the rear retains its normal height, creating the shape of a wedge.
What is the best way to determine if there is an indication of a compression fracture? If there is a crackling sound that occurs when an older individual falls down, this could suggest the presence of a fracture.
In addition, if there’s just lower back discomfort following an accident, but there is no radiating or neuropathic pain on the legs could be a sign of an injury to the compression.
Different Lower Back Pain Conditions Require Different Treatments
* Acute lumbar spinal injury
It is possible to treat the symptoms through rest, medications (medicines to relax muscle) as well as cold compresses (to decrease inflammation).
The majority of people’s symptoms can be relieved by rest, medication and cold compresses, without the necessity of seeing a physician.
However, around 5-percent of sufferers endure chronic pain that lasts for a long time (more than 4 weeks). In this situation it is essential to visit a physician for additional X-rays and Magnetic image (MRI) examinations to look for organic lesions.
* Hernia to the disc
There are five main categories of treatment.
If there’s no sign of muscles being weak or persistently sensation of numbness or numbness in the feet and hands this indicates that the intervertebral disk is not causing nerve compression and that conservative treatment techniques are available:
- Medication Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications like Ibuprofen.
- Physiotherapy: Work out the muscles in the lower back to improve strength or stretch the nerves to relieve of compression.
- Alternative treatments such as massage, acupuncture, and cupping. If the pain doesn’t disappear or signs of nerve compression are evident after attempting the first three methods then it is important to consult a physician in the time frame to receive additional treatment options, including:
- Steroid injections can be instilled directly into herniated discs using the aid of a syringe, which reduces inflammation.
- Surgery: It is an option that is only used in the last instance and over 90% of patients don’t require surgery.
Certain lower back pain conditions must be treated with surgery As Soon as Possible
Generally speaking, surgery is only recommended in cases where the muscles are significantly weak and there is persistent numbness in the feet and hands or if there’s persistent pain that is not relieved after six months after nonsurgical treatments.
In rare instances, surgery may cause complications , like dural tears. While the chances of this being a possibility are very low however, it is recommended to stay clear of it whenever possible. Additionally local scar tissue could develop after surgery, increasing the likelihood of having to repeat the procedure.
However when a patient is experiencing serious neurological symptoms Surgery should be carried out immediately, if possible, in line with security considerations. If not, it could be irreparable to damage the nerve.
Today, doctors typically perform minimally-invasive surgeries using an incision that is two or three millimeters. The surgery greatly reduces discomfort, and patients’ symptoms of muscle weakness as well as swelling of the skin will slowly improve.
A variety of medical journals from professionals indicate that the majority of patients are able to recover after surgery within four months after experiencing muscles weakness. In the following four months some patients may not be able to completely recover even after surgery.
How Do I take care of the Lumbar Spine, and How to Prevent the Lower Back from ache?
The following five tips can assist you in preventing or ease lower back discomfort.
1. Maintain a good posture
Be sure to sit straight and don’t try to lean towards the front.
The following figure shows the amount of pressure placed on the lower lumbar spine in the body of a human, in different positions. The red bars are based on data from a study conducted in 1981 The blue bars reflect data from a study conducted in 1999.
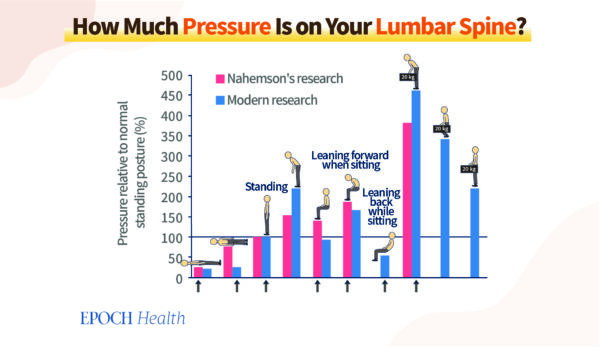
 The amount of pressure placed on the back spine when in different postures. (The Epoch Times)
The amount of pressure placed on the back spine when in different postures. (The Epoch Times)Both studies found that the pressure of the intervertebral disc is at its most minimal when a person is lying flat on their back and disc pressure rises when one lies on their side.
If someone is sitting and leans forward and sitting, the pressure on discs of the intervertebral space is two times as much than when they stand and when one leans back when sitting and sitting, the pressure on the discs’ intervertebral space will decrease. The discs are under pressure. is the highest when one is standing and leaning to the side.
Leaning forward when sitting cause more pressure onto the intervertebral discs in comparison to when standing?
There’s an old Chinese saying that says, “Talking while standing does not cause injury to the back of your back.” It is true that there’s some truth in this claim. Upper body support is provided by 3 forces: abdominal muscles at the front as well as the spine in the middle as well as the muscles of the back at the rear. The abdominal as well as back muscles contract when we stand up, which relieves some tension off of the spine.
It is common for our abdominal and back muscles are relaxed when we sit and lean forward. This leaves only our spine as well as intervertebral discs support the pressure. This increases the risk of developing a herniated disc.
2. Make sure you are using the correct technique when lifting objects that are heavy
Make sure you keep Your spine straight. A lot of people get herniated discs when lifting large objects using an incorrect posture.
Make sure you bend your knees, and ensure that you keep your spine straight when lifting. Use your calves and thighs to lift the weight, not your back muscles.
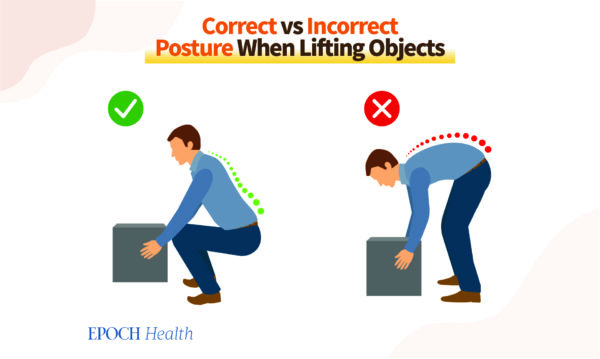
 Flex your knees, and keep your spine straight when lifting. Use the muscles in your legs. (The Epoch Times)
Flex your knees, and keep your spine straight when lifting. Use the muscles in your legs. (The Epoch Times)
3. You should sleep on a firm mattress
It is able to help support the spine.
It is a fact that our back and hips aren’t properly supported when we sleep on a soft mattress that hinders the lower lumbar spine from keeping its natural curve. Thus, back muscles are back muscles are in a tension state and can result in muscle soreness.
4. Use a lumbar pillow
It assists in relaxing muscles in the back. back muscles.
You can place an extra small cushion behind our waist when in a position of sitting or lying down to aid in supporting the natural curve of our lower lumbar spine and ease the tension that run down the back.
5. Stop smoking
Smoking can accelerate disc degeneration.
The nicotine found in cigarettes will block the body’s nutrition from reaching the intervertebral disc. This will speed up the degeneration process thinning, weakening, and thinning. If this occurs the nucleus pulposus of the disc’s intervertebral space is likely protrude.
The X-rays also can reveal whether the patient is a smoker or has a habit. For instance, a patient who develops osteophytes (osteophytes) in a young age or who has thin intervertebral discs may be smoking.

We understand how important it is to choose a chiropractor that is right for you. It is our belief that educating our patients is a very important part of the success we see in our offices.
