Sciatica
can sciatic nerve cause plantar fasciitis
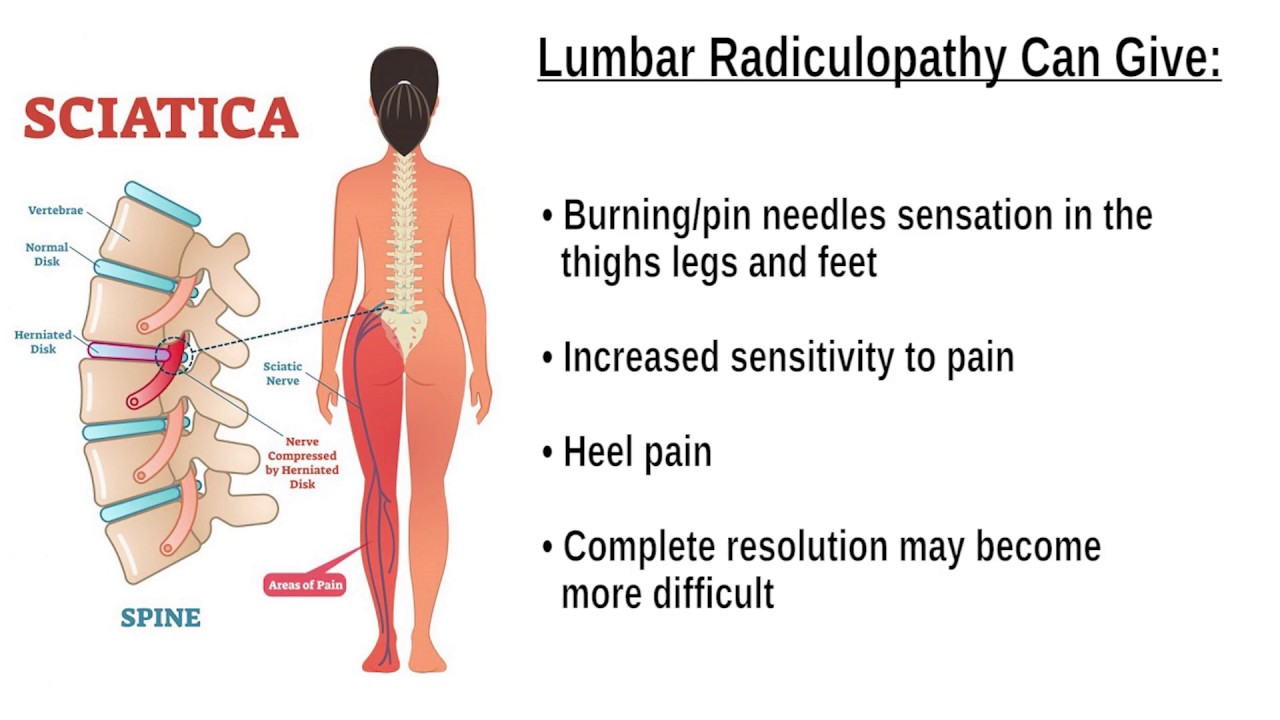
There are two common treatment paths for plantar fasciitis: physical therapy and medication. Unfortunately, both treatments can miss the true cause of heel pain. This means the sufferer may endure heel pain long before receiving relief. Luckily, there are ways to differentiate between plantar fasciitis and sciatica.
Is Plantar Fasciitis Associated With Sciatica?
Both plantar fasciitis and sciatica have similar symptoms and may be confused with one another. In both cases, a thorough physical and visual examination is necessary. The doctor may order imaging tests to see if the sciatic nerve is compressed. A straight leg raise or Lasegue test may also be performed. Treatments for each condition depend on the underlying cause.
Both plantar fasciitis and sciatica can cause heel pain. However, plantar fasciitis is more likely to occur in people with sciatica. In the case of plantar fasciitis, the pain is located in the heel, not in the arch or toes. The pain is usually worse when you stand up after sitting for a long time or when you take your first steps in the morning.
Avoiding overuse and repetitive stress is important if you’re prone to this condition. If you have overpronated or flat feet, you’re at an increased risk of developing the condition. This condition causes overuse and injury to the heel bone. It accounts for two percent of all adult fractures.
Treatment for plantar fasciitis often involves rest and physical therapy. Physiotherapists may recommend exercises for the spine and legs to realign the body and strengthen muscles needed to prevent nerve compression. However, some severe cases may require surgery. For the most part, however, treatment for plantar fasciitis can be managed at home by following a conservative treatment regimen.
Can Sciatica Cause Heel Pain?
If you’re having trouble putting your foot down, you may be suffering from sciatica. It’s important to recognize that there may be something else causing the pain. Often, the pain is caused by a sciatic nerve problem, so it’s important to be careful in stretching, as stretching can worsen the pain.
In addition to sciatica, there are many other causes of heel pain. These conditions include piriformis syndrome, bursitis, and joint dysfunction in the hip and sacroiliac joints. Some patients also experience burning or numbness in the heel. To effectively treat this condition, a treatment plan must be designed that addresses the cause of the pain and the sciatic nerve.
The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis, which results from the overuse of the plantar fascia, which connects the heel bone to the toes. Athletes and people with a job that requires prolonged standing may be at risk for this condition. Other causes include sciatica and tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment options for heel pain caused by sciatica include medications and physical therapy. These treatments can relieve the pain and promote nerve healing. Patients can also opt to use orthotic insoles, which help relieve pressure on the foot. A physiotherapist can also prescribe exercises to strengthen the core and reduce the pain.
Does Sciatica Affect The Bottom Of The Foot?
If you’ve been experiencing pain in your foot, you may be suffering from sciatica. This condition affects the nerves that travel from your lower back to your foot and can be extremely painful. It can also lead to numbness and weakness in the foot and legs. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, you should see a doctor. There are several treatment options for sciatica pain.
First, it’s important to note that sciatica usually starts in one leg but can also affect the other. The pain is typically a burning or shooting sensation but may also be accompanied by tingling and numbness. Symptoms are often worse when the patient gets out of bed or sits for long periods.
Other symptoms of sciatica include weakness in the leg and ankle. These symptoms can make walking difficult and require a referral to an Orthopedic Physician. Sciatica symptoms can be exacerbated by postural compensations, including a shortened, flared foot on the affected leg (referred to as a “duck foot”) and a lateral shift of the spine.
Treatment for sciatica may include medicines or injections to reduce swelling and irritation of the nerve. Surgical treatment is only recommended for severe cases if no other treatment options have worked. Self-care treatment can often provide relief, but it’s still best to seek a doctor’s advice. The doctor will be able to confirm the cause of the pain and recommend alternative treatment methods.
Can Back Issues Cause Plantar Fasciitis?
A physical therapist, chiropractor, or acupuncturist may recommend certain exercises to help heal plantar fasciitis. These exercises realign the body and strengthen the muscles that protect the nerves. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Treatment for plantar fasciitis can also be done at home. It will likely involve rest for up to six weeks and using NSAIDs or a combination of NSAIDs and rest.
Plantar fasciitis typically causes a stabbing pain in the bottom of the foot, usually near the heel. It usually begins with the first few steps in the morning and worsens with prolonged or strenuous activity. The pain may also be worse when walking or standing after sitting for a long time.
People with active lifestyles are at risk of developing plantar fasciitis. People who stand for long periods and wear shoes that do not provide proper support may develop this condition. Overweight people are also at risk of developing plantar fasciitis. A common cause of this condition is overuse or trauma to the foot.
Plantar fasciitis usually results from a biomechanical problem that causes abnormal pronation. For example, a patient with a flexible rearfoot varus may appear to have a normal foot structure, but when they stand, significant pronation occurs. This abnormal pronation increases tension on the plantar fascia and affects how weight is distributed when standing.
What Nerve Is Involved In Plantar Fasciitis?
When you develop plantar fasciitis, two main nerves are involved in the condition. One is called the calcaneal nerve, which is located at the base of the heel and innervates the abductor digit and flexor muscles. The other nerve is the lateral plantar nerve, which runs along the inside and outside of the arch.
Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition that affects the foot’s arch. There are two major types: neurogenic plantar fasciitis and true plantar fasciitis. Both are characterized by pain on the arch side of the heel that increases with weight bearing. Unfortunately, many physicians cannot differentiate between the two, and patients may experience both types of pain.
Fortunately, the majority of patients respond to conservative treatment. However, if treatment fails to relieve pain, the patient should be evaluated for entrapment of the nerves in the tarsal tunnel. Baxter’s neuritis is caused by the inferior calcaneal nerve (ICN) turning at an angle in the plantar fascia between the abductor hallucis and quadratus plantae.
A lateral plantar nerve branch entrapment can also cause pain in the heel. This is common and is the cause of most cases of plantar heel pain. However, it is important to distinguish between plantar fasciitis and nerve entrapment because the two conditions can present similarly.
What Part Of The Foot Hurts With Sciatica?
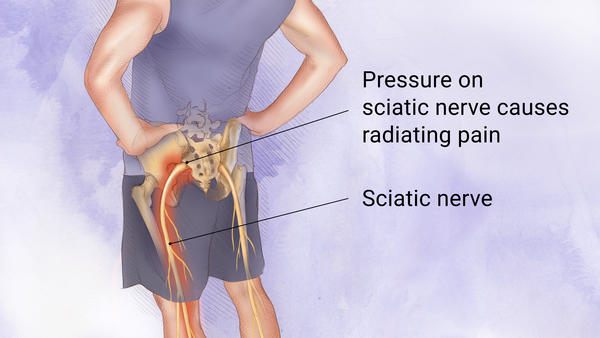
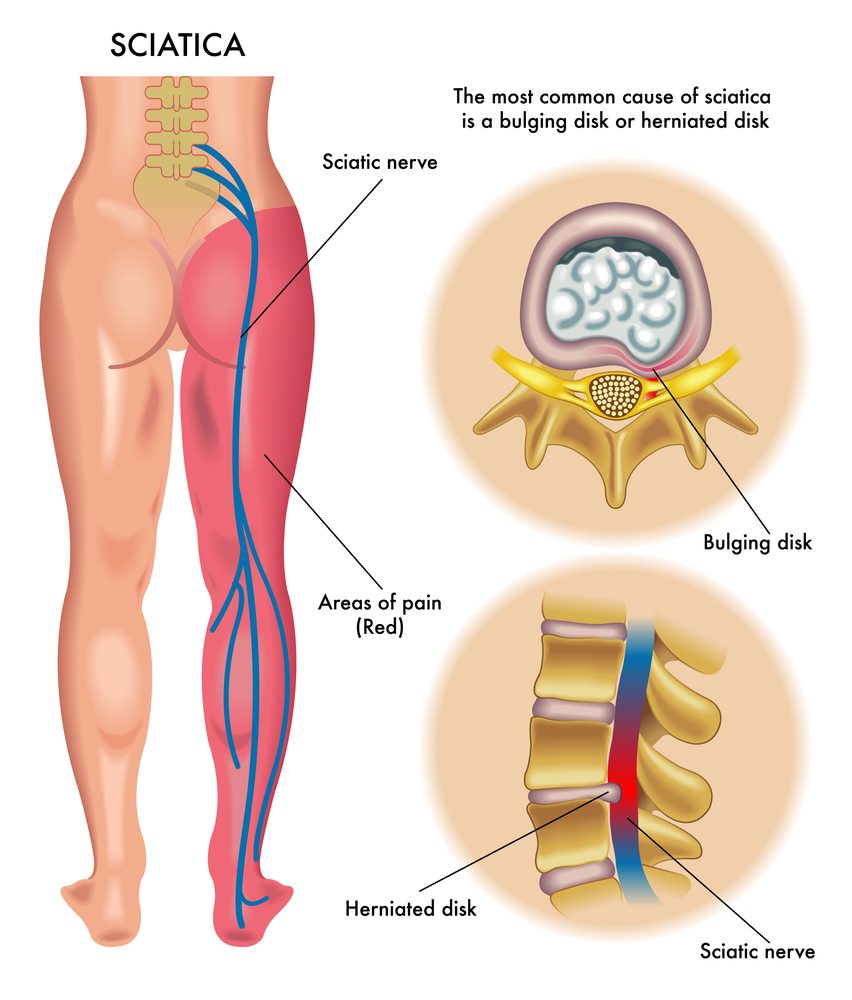
Sciatica is a painful condition that affects the legs, hips, and feet. It is caused by pressure on the sciatic nerves. The sciatic nerves are located in the lower back. These nerves run through the hollow spinal column and carry messages. Any pressure or damage to these nerves will cause pain and other symptoms.
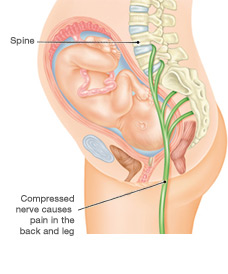
A herniated or slipped disk can press on the nerve. About 1% to 5% of people in the U.S. will experience a slipped or herniated disk at some point in their lives. This condition weakens the outer wall of the disk and causes the center portion to bulge. If this happens, pressure will apply to the sciatic nerve, making it painful and numb.
Sciatica symptoms vary by location and severity. The pain typically extends down one side of the body from the spine and can be sharp, tingling, or burning. The pain is often accompanied by numbness, weakness, and leg weakness. Sciatica symptoms can be found anywhere along the leg but most often occur in one leg.
There are many causes of sciatica, and each person has a unique cause. However, if the sciatic nerve is inflamed or injured, it can radiate pain down one or both legs. This pain may also cause muscle weakness, numbness, or a pins-and-needles sensation.
Conclusion
If you have sciatica, you have nerve-induced pain in the lower back. Nerve pain in the foot may also occur due to nerve damage from systemic conditions, such as diabetes or multiple sclerosis. This often sends shooting pain down your legs and feet. You can directly see the relationship, and you don’t need to be a physio or doctor to understand how your foot pain might be sciatica waiting to happen.
It will also make sense for you who have suffered from heel and foot pain to go on then and suffer from sciatica. It is known colloquially as a trapped nerve, though this may also refer to nerve root compression (by a slipped disc, for example). As with other nerve pain, you might feel tingling or numbness, which can differentiate sciatica from plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis pain is typically limited to your foot’s heel and arch.
The location of pain from arthritis can be confused with plantar fasciitis pain, and the occurrence of pain can be similar. It has been reported that plantar fasciitis occurs in two million Americans yearly and 10% of the population over a lifetime. Plantar fasciitis occurs in men and women but is more common in the latter.
A posterior calcaneal spur may also develop on the back of the heel at the insertion of the Achilles tendon. Several factors can cause knee pain. Awareness and knowledge of knee pain causes lead to faster diagnosis and treatment. Knee pain can be related to the knee joint or around the knee. Foot pain- may be caused by many different conditions or injuries.

Doctor Osvaldo Pepa, Neurosurgery Service Physician at Hospital San Martin, La Plata, Argentina. I graduated last November 16, 1984 with a Medical Degree at the Universidad Nacional de La Plata. The Medical Board of La Plata, District 1, licensed me as a Neurosurgeon in 1990. I hold a Provincial and National License and an active member of the Neurosurgery Society of La Plata, World Ozone Therapy Federation, and Inter American Society of Minimally Invasive Surgery.