Sciatica
Do muscle relaxers help sciatica
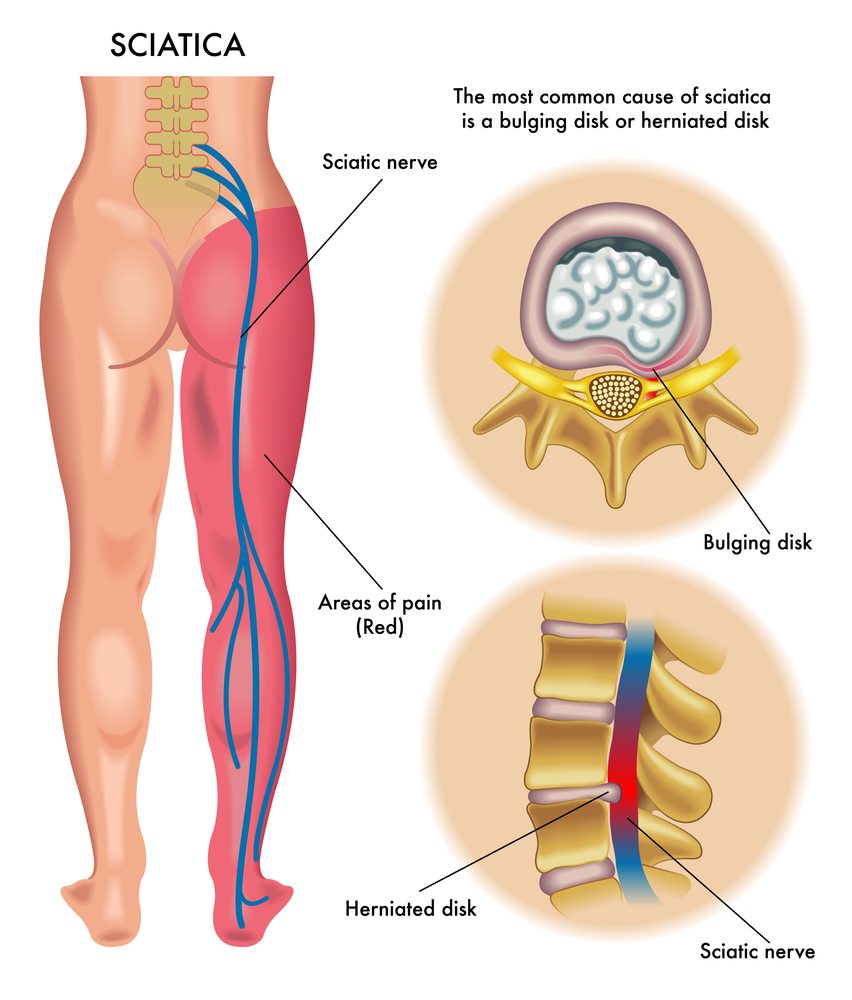
Sciatica is a condition that results in pain, tingling, or numbness in the lower back and legs. This condition can be caused by various factors, including muscle spasms, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis. Muscle relaxers are often prescribed to help relieve the symptoms of sciatica.
How Can Muscle Relaxers Help Sciatica?
NSAIDs, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants can be effective treatments for sciatic nerve pain. These drugs can be over-the-counter or available by prescription. Other medications that can relieve sciatica pain are anti-seizure and tricyclic antidepressants, which a doctor prescribes. Acupuncture, which involves inserting tiny needles into specific points on the body, can also help. Some patients find relief by undergoing spinal manipulation by a chiropractor. In some cases, sciatica symptoms diminish within a few days. Sometimes, the flare-ups recur intermittently for weeks or months at a time.
When treating sciatica, patients should consult a physician and physical therapist. Often, the pain can be caused by a spinal condition, such as a herniated disk, a bone spur, or spinal stenosis. Other causes of sciatica include restless leg syndrome, piriformis syndrome, multiple sclerosis, or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Muscle relaxants may be prescribed for patients suffering from chronic sciatica, although these drugs are not more effective than a placebo. They may be used to treat a more serious condition, such as multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disease wherein the immune system attacks certain body parts. In addition to these medications, the pain can be treated with physical therapy or physiotherapy to correct posture or strengthen lower back muscles. Other treatments, such as spinal manipulation, are as effective as pain medication.
Which muscle relaxant is best for sciatica?
The correct treatment for sciatica will vary from person to person. Some people find muscle relaxants help with the pain, while others do not. In general, though, the pain is less severe with muscle relaxants than NSAIDs. Although muscle relaxants are generally safe and effective, they can sometimes be side-effect-prone. In addition, they can cause dizziness, dry mouth, and confusion in older patients.
The goal of treatment for sciatica is to reduce pain and improve mobility. Simple self-care measures such as applying an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel can help reduce pain and swelling. Another great home remedy is hot packs. A hot pack can reduce pain and inflammation and be applied to the painful area several times a day. Another common home remedy is applying a hot pack to the affected area.
Despite the positive side effects of muscle relaxants, you should always discuss the treatment with your doctor and other healthcare providers. Using muscle relaxants should be only a part of a comprehensive plan for your spine health. They should be a last resort. Ultimately, they should only be taken in the presence of a diagnosis of sciatica. And remember, understanding the treatment options available to you is your best defence against back pain.
Will muscle relaxers help nerve pain?
While muscle relaxers may be a good choice for some sciatica sufferers, they may not be a suitable solution for everyone. Inflammation is one of the main causes of sciatica pain, and treating it with anti-inflammatory drugs such as NSAIDs, tricyclic antidepressants, or anticonvulsants can be extremely helpful. However, they are usually only used on a short-term basis, and you should only take them as directed. The oral steroid prednisone provides pain relief by reducing inflammation.
While physicians commonly prescribe muscle relaxants to alleviate acute low-back pain, they do not do much for long-term sciatic pain. Muscle relaxants may reduce the pain if they do not treat inflammation, but they can also cause side effects. Muscle relaxants are also known to cause drowsiness. They are most effective in preventing muscle spasms but should only be used if the symptoms are temporary and they are not appropriate for prolonged use.
Muscle relaxants can relieve acute sciatica by reducing back pain caused by spasms in the muscles of the lower back and leg. They can also help reduce muscle spasms, which can be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as a disc problem. In severe cases, surgery may be required. Although surgery is a last resort, it can help patients with sciatica. Muscle relaxants have potential side effects and may be ineffective for people with heart, liver, or kidney problems.
How do I get my sciatic nerve to stop hurting?
Self-care measures such as resting the affected area can help relieve sciatica. While prolonged inactivity can worsen the condition, resting may offer relief. Other self-care options include applying cold or ice to the affected area. You can try frozen peas wrapped in a towel if the rest is ineffective. But never use either of these techniques while sleeping. The pain is likely to return.
A specialized stretching exercise can help you relieve the pain. The sciatica stretch is a simple technique that stretches the gluteal and piriformis muscles. These muscles are inflamed and press against the sciatic nerve. Leaning over the affected leg and pulling it across the body can help. This stretch is best performed for 30 seconds at a time.
Proper sitting posture is crucial for relieving sciatic nerve pain. If your sitting position is too low, you should try a chair with built-in lumbar support. Otherwise, a lumbar roll cushion can support the lower back and relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve. Avoid prolonged sitting, as this can worsen sciatic nerve pain. Sitting often causes tight muscles that support your pelvis and lower back. Take frequent breaks if you need to stay in a chair for too long.
Does it affect muscle spasms?
Yes, but not for everyone. Some sufferers can get temporary relief with over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or paracetamol; in more severe cases, prescription drugs may be required. These may include stronger NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, antidepressants, and anti-seizure medications. In some instances, acupuncture (the practice of inserting tiny needles into specific points on the skin) may be an effective treatment. Chiropractors may also provide relief by performing spinal manipulation.
Muscle relaxants work by relaxing tight muscles and reducing muscle spasms. This may be caused by a disc problem or inflammation of the lumbar muscles. Although muscle relaxants help reduce back stiffness, they may not be the most effective treatment for sciatica. In addition to the risk of side effects, muscle relaxants can also lead to drowsiness. So, speaking with a doctor is important to find the best treatment for you.
Physical tests can reveal the source of sciatica. The doctor will likely perform reflex and muscle strength tests to rule out other issues, such as a herniated disc. Imaging tests can also detect a bone spur or herniated disc. Doctors often don’t order imaging tests for sciatica unless the pain persists. An X-ray is an important tool to diagnose and treat sciatica.
Is it good for Sciatica pain relief?
Yes, but only if you are suffering from a sciatica flare-up. While these drugs are a quick fix to reduce pain and inflammation, they do not provide long-term solutions to sciatica. Although they can reduce pain, they do not cure the condition and may even lead to secondary ailments.
NSAIDs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are an effective treatment for sciatica. These medications are widely available and are marketed to relieve pain by reducing inflammation. However, NSAIDs have side effects, which make them inappropriate for patients with underlying medical conditions. In addition, NSAIDs may irritate stomach tissues, so they should be used in moderation. Another common method of sciatica pain relief is acupuncture, which involves inserting tiny needles into specific points on the body. This procedure can be effective for short-term pain relief but can cause skin irritation and should be avoided for long-term use.
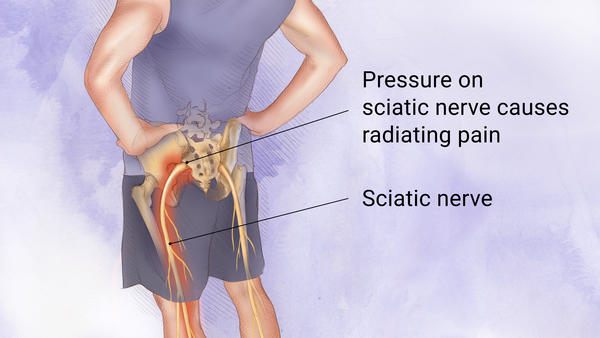
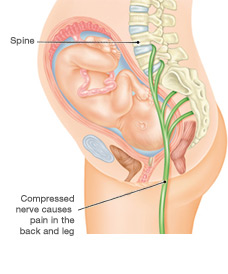
Sciatica, medically known as lumbar radiculopathy, is caused by pressure on or irritation of the sciatic nerve roots in the lower lumbar spine. This pressure causes severe pain, numbness, and weakness that starts in the lower back and radiates down, causing leg pain. It is caused by problems with the nerve which travels through the legs and feet. The sciatic nerve can become compressed due to a herniated disc. Age-related bone spurs and a pelvis fracture can also cause compression of the sciatic nerve.
Do muscle relaxers relax muscles?
You might consider a prescription muscle relaxer if you’re looking for a safe and effective way to treat muscle pain. Muscle relaxers, also known as spasmolytics, work by inhibiting neuromuscular activity. In most cases, they can be taken to relieve spasticity and temporary paralysis of muscles caused by neurological problems. Muscle relaxers can help treat this condition, but you should consult your doctor before using them.
You may be aware that muscle relaxers do not relax the muscles. They work by affecting the central nervous system, causing general sedation. Before taking a prescription, it’s important to learn the facts about muscle relaxers. You may have been taking muscle relaxers without realizing it.
Most muscle relaxers are effective for short-term use, but there is always a risk of misuse and addiction. Several types of muscle relaxers are available, and you’ll likely need to try a few before finding the right one for your situation. But don’t let that stop you from getting help for your muscle pain! You can try natural muscle relaxers instead. These are less addictive and can also heal your muscles.
Conclusion
A specialist should be consulted if sciatica symptoms are severe or progressively worsen. Cold compresses or ice packs can be applied to the painful area for 15 to 20 minutes in order to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. A heat compress or pack can relieve pain by increasing circulation and loosening tight muscles. It may be advisable to consider spinal cord stimulation if physical therapy, medicine, or even surgery does not relieve your back pain. This advanced treatment boasts a high success rate.

Doctor Osvaldo Pepa, Neurosurgery Service Physician at Hospital San Martin, La Plata, Argentina. I graduated last November 16, 1984 with a Medical Degree at the Universidad Nacional de La Plata. The Medical Board of La Plata, District 1, licensed me as a Neurosurgeon in 1990. I hold a Provincial and National License and an active member of the Neurosurgery Society of La Plata, World Ozone Therapy Federation, and Inter American Society of Minimally Invasive Surgery.